There are many tutorials that can teach you how to write a blog post.
They can educate you on the mechanics of blogging, what to do, and what not to do. 456
Read through them and you can learn how to craft a perfectly serviceable blog post. Heck, you might even write something that wins you an adoring fan or two.
But if you dream bigger, if you want to know how to write a successful blog post that cuts through the noise and wins you legions of fans, you need something better than a run-of-the-mill tutorial.
You need an ultimate guide.
In this post — this ultimate, step-by-step guide — we’ll share tips used by professional freelance writers to create spellbinding posts that are adored by thousands. You’ll learn the secrets to crafting irresistible headlines, seducing introductions, captivating advice, and motivational closings.
You’ll even learn how the pros refine and polish their posts once they’re finished writing them.
These are secrets many bloggers would gladly pay real money to learn, but it won’t cost you a thing — other than a few minutes of your time.
1. Craft a Great Headline That Readers Can’t Resist

Want to know one of the biggest mistakes bloggers make?
Writing blog posts before the headlines (aka the post title).
Without a headline, they have no roadmap to follow. And so their post goes in multiple directions, leaving readers feeling dizzy, confused and disoriented.
And then they try to create a headline that embraces all that madness. Bloggers, have mercy!
If you want to write a great blog post full of clarity, conciseness, and conviction, spend some time crafting a blog title that sets a clear destination, lures readers in, and leaves them eager for your advice.
Your blog title will be your map, your writing navigation system, letting you know which literary roads to choose and which to avoid so that readers reach the intended destination as easily and efficiently as possible.
Follow these 8 rules to craft your killer headline:
Headline Rule #1. Pick a Mouth-Watering Topic
Want your blog post to get opened?
Then your headline must promise readers the very answer to whatever is tormenting them. The thing that keeps them up at night.
Your headline should not promise them a trip to the moon and back — readers are way too swift for such shenanigans. Keep the benefit specific and narrow, and readers will feel compelled to click and get the solution to what’s bugging them.
How do you find out what’s bugging your readers? How do you know which of your many blog post idea (we know, you have many) should be pursued?
Research:
-
Review comments on your posts and on posts of other sites in your niche.
-
Send your subscribers surveys asking them what their greatest struggles are.
-
Use tools like BuzzSumo to find out what the most popular posts in your niche are (which gives insight into your target readers’ needs).
-
Read the reviews of books in your niche on Amazon (you’ll find a gold mine of feedback to explore).
You have one responsibility as a blogger — yup, just one. And that is to serve your audience. The better you know them, the better you serve.
Before you know it, you’ll know them so intimately they’ll feel like you’re reading their minds, and your headlines will reflect that.
Example:
Let’s say you’re in the self-improvement space and you wrote the headline below:
How to Create an Amazing Life
This headline is so broad it’s unlikely to draw readers in. No one loses sleep over “wanting to create an amazing life.” They lose sleep over specific aspects of their lives that have left them unfulfilled.
So you are better off narrowing in on something specific that’s bugging your readers, such as:
How to Boldly Pursue Your Dreams Even if You’re Scared and Insecure
Narrowing in on something specific makes readers feel like you have the answers they’re looking for.
Headline Rule #2. Steal from the Pros
Okay, you’ve done your research and you know exactly what your readers need. Now it’s time to turn your topic into a killer headline.
The easiest way to master the art of writing headlines?
Steal.
Not in the unethical way. In the smart and efficient way.
Decades of copywriting and advertising research have revealed the types of headlines that have proven to be successful. The types of headlines that zap readers out of their info-overload comas and compel them to open. Why mess with that research?
If you want your headlines to grab readers, stick with what works.
No, your headlines don’t need to sound like they came straight from BuzzFeed. They can reflect your voice and style.
But until your writing skills match Jon Morrow’s, let the proven templates be your guide (how do you think he got so good at writing headlines?).
Blogging is hard enough, so if you have templates at your fingertips, why not use them?
The easiest templates to start with? “How to” headlines and list post headlines. They are classics and they work. In fact, 75% of Smart Blogger’s most popular posts use these formats.
Examples:
Here are a number of Smart Blogger headlines that follow the “how to” and list post templates.
“How to” Headlines:
List Post Headlines:
Note: You can download Jon’s free 52 Headline Hacks, where you’ll find more template options than you’ll ever need.
Headline Rule #3. Engage Your Senses
Vague headlines leave readers feeling empty. Tangible headlines leave them feeling understood.
How do you create tangible headlines?
Put yourself in the shoes of your reader.
How do they feel? What do they see, taste, or smell? What do they hear?
Engage all of your senses by using sensory words. The more your headline gives voice to their exact experience, the more they’ll feel like your quality content was written for them.
Example:
Let’s say you blog about health and wellness and you wrote a headline called:
5 Steps to Take When a Migraine Hits
This headline follows a proven list post formula, and it narrows in on something that’s bugging readers. All in all, it’s not too bad.
But it could be even more concrete.
To step it up a notch, put yourselves in the shoes of your readers. Think about exactly what they’re experiencing.
Perhaps that would lead you to the following:
5 Ways to Soothe Pounding and Blinding Migraines
If you suffer from migraines, there’s no way you could resist clicking such a headline.
Headline Rule #4. Tease, Don’t Satisfy
A common mistake you may not even realize you’re making?
Giving away too much in your headlines.
Your headlines should lure readers in like a literary temptress. They should catch readers’ attention and invoke their curiosity, not give a solution.
Give a solution in your headline and readers feel no need to go any further — they’re bored by the very thought of your post.
When this happens, not only do you lose but your readers lose as well, as they trade the richness of your perfect blog post’s advice for the quick fix offered by the headline.
Hello World.
Example:
Let’s say you blog about personal finance and you write the headline below:
How to Save for Retirement by Creating a Monthly Budget
Sadly, readers will see this and think they’ve got all the advice they need — if they want to save for retirement, they must create a monthly budget. No need to read more.
On the other hand, a possible revision could be:
How to Save for Retirement When You’re Living Paycheck to Paycheck
For anyone living paycheck to paycheck, this headline would pique their curiosity. Nothing is given away, it speaks to an audience with a very specific problem, and it promises a solution they’d love to get their hands on.
Headline Rule #5. Honor the Headline Commandment
When it comes to headlines, there is only one commandment you can never break:
“Thou shalt not deceive.”
This may seem obvious, but writers inadvertently do it all the time.
How?
They over-promise.
Big no-no. The content of your post must fully deliver on exactly what the headline promises.
If the post only delivers part of the solution, readers will feel misled and lose their trust in you.
Let’s never do that to them, yes?
Examples:
Let’s say you write a post called:
How to Live a Happy and Peaceful Life
But then the post only talks about following your dreams, which is really only one aspect of living a happy and peaceful life. Even though you didn’t intentionally deceive them, readers will feel shortchanged. You might as well have written an over-the-top “clickbait” headline — your readers would have been as equally disappointed.
Another example…
Perhaps you write a post called:
5 Killer Ways to Attract New Clients to Your Coaching Business
But then the fifth way contains no useful advice and instead leads to a sales page to get the solution … no bueno.
Headline Rule #6. Trim the Fat
Want to overwhelm readers right from the start?
Fill your headline with weak and flabby words.
What are weak and flabby words? Empty, unnecessary words that add no real value. Instead, they create clunky phrasing and leave readers scratching their heads in confusion.
The mistake many bloggers make is writing headlines the way they speak. While that’s okay when you write the post (to a certain extent), when you write headlines that way, it waters them down.
You want your headlines to be as ruthlessly concise and powerful as possible. So chop out weak words and throw in power words (if appropriate).
Examples:
Let’s say you draft the following headline:
How to Find It In Your Heart to Forgive Someone Even if They’ve Hurt You Really Badly
There are just so many words! We can cut them down as follows:
How to Forgive Someone Who Hurt You Badly
We can then add some power to it:
How to Forgive a Soul-Crushing Betrayal
Much better.
Another Example:
Here’s a mouthful:
How to Stop Being Overly Doubtful of Yourself So You Can Finally Begin to Pursue Your Wildest Dreams
My head is spinning. This can be cut down to:
How to Stop Doubting Yourself and Pursue Your Wildest Dreams
We could even make it more tangible and powerful:
How to End Paralyzing Doubts and Conquer Your Wildest Dreams
Nice and trim, but packs a punch.
Headline Rule #7. Don’t Be a Smarty-Pants
Your headline should make sense to all readers no matter where they’re coming from or in what context they’re approaching your post.
They shouldn’t have to guess what the benefit is. After all, you’re supposed to be reading their minds, not the other way around.
So you’ll want to avoid using metaphors (unless their meaning is painfully obvious), jargon, rhymes, made-up terms, or anything that tries to be overly clever or complicated when drafting your headlines.
Examples:
Where to begin with this one:
How to Be Happy Without Acting Sappy
A headline like this tries to be too clever — readers don’t give two hoots about not acting sappy, obviously. Don’t prioritize cute tactics like rhyming (or even alliteration) over-delivering clear benefits in your headlines.
How to Raise a Child That Is the Apple of Your Eye
A headline like this is also trying to be too clever. “Apple of Your Eye” is a common metaphor readers are likely familiar with, but there’s no concrete benefit being offered here. A headline must always contain a strong benefit, not a cute phrase.
How to Follow the Path of Glory to Your Success
No clue what this means … and I just wrote it. If there isn’t a singular and clear interpretation of what the headline’s benefit is, it’s trying too hard. So save the metaphors for the actual post where they will (hopefully) make more sense.
How to Stop Treating Love Like a Captive Animal
Perhaps you effectively explain in the post how people treat love like a captive animal, and it may make for a great analogy, but readers scanning headlines will have no clue why they should stop to read this, and so they likely won’t.
Headline Rule #8. Rock Your Style
The more consistent you are with your audience, the more trust they’ll feel for you.
If you generally keep your headlines pretty simple and then suddenly write one jam-packed with power words, your readers will feel confused.
The more you write, the more of a writing style you’ll develop. Once you determine what that style is, use it consistently (or make slow and gradual changes to it if necessary) so your audience learns and trusts your brand.
Example:
If most of your headlines read like this:
Then you might not want to suddenly write a headline that reads:
Your readers will think your blog got hacked!
How to Write a Headline: Bonus Tip
When writing a headline, try crafting 5–10 different versions of the same headline.
The more you play with the words, the better you will get at creating clear, concise, and curiosity-invoking headlines that readers cannot resist.
Editor’s Note:
I’d be remiss if I didn’t discuss a question we hear often:
“How long/short should my headline be?”
Ever notice how some headlines in SERPs (search engine results pages) are truncated?
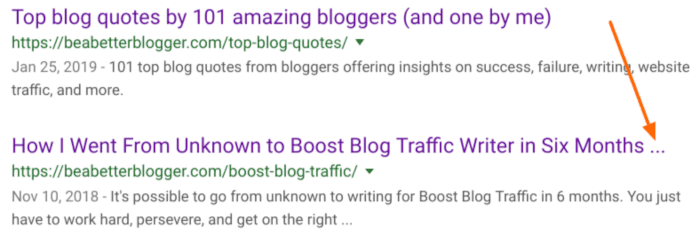
It’s based on your headline’s width in pixels (a free tool like SERPsim will show your headline’s width), but as a general rule:
At right around 60 characters, Google will cut off your headline.
Since a truncated headline can result in fewer people clicking your link in SERPs, it’s a common SEO practice to keep your headlines 60 characters or less.
Of course, things are never that easy.
In a recent study, Brian Dean of Backlinko found that longer (14-17 words) headlines generated more shares on social media than shorter headlines.
(76.7% more social shares, to be exact.)
As with all things, your mileage may vary.
2. Write an Introduction That Grabs and Seduces

You’ve lured readers in with your headline. Now you’ve got to keep them.
No easy task, my friend.
Readers are fickle. Known to take a quick glance and then vanish from your online sanctuary, lickety-split!
You must fight to keep them there, and the way you craft your introduction plays a huge role in their browsing commitment.
Follow these rules to craft an introduction that captivates your readers:
Introduction Rule #1. Slip into Their Shoes
A common mistake that reeks of amateur blogging?
Trying to sound too academic in your blog openings.
You know, those posts that start like this:
“Research has proven that 92% of people fail to achieve their goals because they are unable to create and stick to habits that support those goals …”
Don’t get me wrong — as a lawyer, I value solid research. But in the blogging context, this approach bores readers. If you want to captivate instead of bore, you must make readers feel like you’re reading their minds.
A powerful way to achieve this?
Empathy.
Step into the shoes of your target audience and write from their perspective. Show them you understand exactly what they’re going through.
After all, you likely struggled with the very topic you’re writing about and learned how to overcome it. We teach what we most wanted to learn, right?
So show readers that you “get it.” You’re not some corporate slog, you’re in it with them, fighting the good fight and sharing the tools that brought you to the other side.
Example:
This introduction is a masterclass in empathy:
Do you feel that? That little tugging sensation on your heart? You’re not sure what, but something is pulling you to change. Not in a confess-your-sins-oh-ye-sinners way, but to shift directions, to embrace your calling, to finally do what you were put here to do: Write. You feel the ideas inside you. You sense them straining to escape. You know your job is to set them free, firing them like a cannon into a world in desperate need of them. But you’re afraid. You’re afraid of quitting your job and living without a safety net. You’re afraid of the concerned, disapproving looks your friends will give you when you tell them you’re giving it all up to write for a living. You’re afraid of not having enough money for food, of the power being cut off, of watching your family shivering and hungry, all because of your “selfishness”. And most of all? You’re afraid you’re wrong about yourself.
As writers, we all share the deep longing to embrace our calling and express our ideas, but we also share the fears that so often sabotage those longings — the fear that we don’t have what it takes, that we’ll crash and burn, and that our dreams are just that — dreams.
In his introduction, Jon addresses all those longings and fears and immediately makes you feel like he gets you so intimately, it’s almost creepy.
Creepy, but effective.
Note: You don’t need to open like this in every post. There are certainly other approaches, like telling a powerful story. But if you’re working on mastering your craft and getting the most impact for time invested, an empathetic opening is an approach you’ll want to use frequently.
Introduction Rule #2. Get into Character
If you want to captivate readers, you must trigger their emotions.
So as you sit down to write, think of the feelings you want them to experience:
Fear, anger, sadness, hope, joy, disgust, shame, comfort, love, courage, and so on.
Then get into character and feel them yourself as you write, and your words will read with undeniable authenticity.
When Lin-Manuel Miranda wrote the heartbreaking lyrics in Hamilton that have left tears on the faces of millions, it was his eyes that first shed tears as he put his pen to paper.
So play with your emotions. Map out the emotional journey you’re taking readers on, and infuse those feelings into your writing. Feel what you want your audience to feel and your words will exude those emotions.
This tip applies to your whole post, but in no place is triggering your audience’s emotions more important than your introduction.
You feel me? 🙂
Example:
I once wrote an emotional post about my two little girls which addressed how delicate their emotions are, as well as my own vulnerabilities and my longing to give them the patience, presence, and love they deserve.
Here’s a portion of it:
I told my three-year old daughter as we stood outside the car in her school parking lot, the rain pouring down on us as she sobbed breathlessly in my arms. She didn’t want to go in the car. She just wanted me to stand there, holding her. And I didn’t want to rush her, or tell her to stop crying. “I’ll hold you for as long as it takes.”
I felt that longing intensely and definitely shed some tears as I wrote the introduction. The feedback I got from readers was that they felt the same intensity, and even cried as well.
When we write, our feelings seep into our words.
Introduction Rule #3. Lure Readers Down the Page
Want readers to commit to your post?
Accelerate their experience. Lure them down the page.
The faster they get pulled down, the more committed they’ll feel.
Too many bumps in the road early on, and off track they go, never to return.
Here are three writing tips to use in your intros to lure readers down the page:
#1. Open With a Short Sentence or Question
Kind of like how I opened this section. 🙂
This is how all of Smart Blogger’s posts open, and for good reason. It’s a copywriting technique proven to pull readers in.
Start a post with a long clunky paragraph and they’ll feel exhausted just looking at it.
#2. Take a Knife to Your Words
Slash as many words as possible.
If the first draft of your introduction is 200 words, try cutting it down to 100. The more you practice this, the more efficient your blog writing process becomes.
And when you write efficiently, your words have power. That power will grab your readers.
#3. Set the Rhythm
All writing has a pace and rhythm.
You want your introduction’s pace and beat to be somewhat quick. You can slow things down later.
How do you achieve this?
-
Use short sentences. Even sentence fragments (totally okay).
-
Make your paragraphs no more than one to three sentences long.
-
Use delayed transitions to weave sentences together.
-
Make each sentence and paragraph lure readers into the one that follows.
-
Read the post out loud to check the flow. Are things moving forward smoothly or stalling?
The best writers, like the best music composers, take readers on a journey. Fast and slow, loud and soft, urgency and ease.
The more you pay attention to this, the more rhythm you’ll infuse into your words.
Example:
Shane Arthur sends readers’ eyes flying down the page by using crisp sentences and short paragraphs to create a fast rhythm:
You’re not stupid. You know what writing is truly about. It’s a never-ending battle for your readers’ attention. Every sentence is a link in a taut chain that connects your headline to your conclusion. And you are just one weak sentence away from losing your reader forever.
He then appropriately slows things down in the section that follows with longer sentences. A masterful composition!
Introduction Rule #4. Make Them Beg
Want readers begging for your solutions?
Add a little fear to your opening.
What are readers worried about? Do they know what will happen if they don’t solve the problem the post is addressing? What is the worst-case scenario?
Bring those fears to the surface. Expose them.
By doing so, not only will readers feel a camaraderie with you (because you understand their fears, so clearly you’ve tip-toed through the dark side yourself), but they’ll feel more eager than ever for the solution you present.
We all have fears. We think we need to hide them, but the more we give voice to them, the easier they are to set free.
Do that for your readers.
Example:
In his introduction, Glen Long brilliantly taps into the fear of failure all writers experience by addressing the dream of making a living as a writer and then quickly smothering that dream with the doubts that creep up at the mere thought of it:
So, who knows? Maybe the doubters are right. Maybe you are naive to think you could earn a living doing something you love, instead of something you just tolerate.
The fear of failure is painful, yes. But giving voice to it is validating and makes readers eager for the solutions that will set that fear free.
Introduction Rule #5. Hint at the Promised Land
Finally, as you wrap up your intro, hint at the promised land.
The place readers will get to when they master your methods. The destination your post promises to take them.
But whatever you do, do not give it all away. Just one sentence that says too much satisfies your readers enough to send them clicking away.
Why? Because readers bore easily. You must keep them on their toes. And the point of an introduction is not to give answers, it’s to set the stage for all the hearty advice your post will provide.
Example:
In the introduction to Meera Kothand’s post, she addressed a problem all new bloggers face: How do you get to know your audience when you don’t have one yet?
She goes on to talk about the big mistake many of them make (making assumptions) and why that’s ineffective. Then, she uses the simplest phrase to hint at a solution:
That kind of guessing is like throwing darts blindfolded and hoping you hit the bull’s eye. Sometimes it works. Usually, it doesn’t. Fortunately, there’s another way…
How could anyone not want to keep reading?
How to Write an Introduction: Bonus Tip
When writing an introduction, try drafting two completely different versions approached from different angles and triggering different emotions.
Doing so will highlight the techniques and emotions that work best for both your audience and the content of your post.
Editor’s Note:
A word of caution:
No matter how eloquent your words…
No matter how powerful your prose…
If your introduction doesn’t satisfy search intent, readers will click the “back” button and never return.
What’s search intent?
It’s the purpose behind the Google search.
If someone searches for “how to lose weight” in Google, they’re expecting search results that will help them lose weight.
If they click a headline that reads “7 Easy Tips For Losing Weight Fast”, and the post begins with an amusing Nicolas Cage anecdote, there’s a good chance they will leave — never getting to read the rest of the post, which is filled with weight loss wisdom.
And when they leave, what they’re essentially telling Google is this:
“At no point in your rambling, incoherent response were you even close to anything that could be considered a rational thought. Everyone in this room is now dumber for having listened to it. I award you no points, and may God have mercy on your soul.”
And Google will respond by ranking your post lower in its search results.
Search intent is a big part of SEO (search engine optimization). When we do keyword research here at Smart Blogger, figuring out the keyword phrase’s intent is one of the first things we do. It shapes our headline, meta description, introduction, word count, and more.
The ins and outs of mastering it would be an article all by itself, so we’ll simply say this:
Taking the time to analyze the results in Google so you have a solid handle on why people enter the particular query your blog post will be targeting is time well spent. Figure out the intent, and then make sure your intro matches it.
3. Deliver Advice That’s Easy to Consume and Impossible to Ignore

Okay, you’re doing great.
You got readers to click on your headline, you lured them down the page with your intro, and now it’s time to deliver on all that you’ve promised.
If you want readers to love you and look forward to every good blog post you write, you’ll over-deliver.
If you want them to take a quick look and vanish for good, you’ll under-deliver.
The choice is yours.
Use the guide below to deliver valuable and easy-to-consume advice:
Content Rule #1. Add Pitstops
Subheads — use them.
Why? Because readers are scanners.
They have no choice. There’s a behemoth amount of content at their fingertips, and not all of it is good.
And so they scan (as do you, I’m sure).
Subheadings are your chance to prove to readers that your content holds value. To keep luring them back into your post, when their instinct is to leave.
Blogging is a battle, remember?
Keep these four tips in mind when drafting your subheads:
#1. Add a Subhead Every Few Paragraphs
Sprinkle subheaders throughout your post.
Why? Because they gently guide readers along the route your post is heading, making their experience feel clear, easy and enjoyable.
And never forget, your blog posts are all about your readers’ experience.
If readers see too much text when they’re scanning without enough pit stops, they’ll feel overwhelmed. It’s like getting on a bus tour and being told there will be no bathroom breaks … oh, the anxiety!
Example:
Every single post on Smart Blogger.
Seriously.
That’s how important this is.
#2. Avoid the 3 Subhead Blunders That Make Readers Bounce
Subheads have the same function as headlines; they must make readers curious so they keep reading. So you should follow similar rules when drafting them and avoid the following common blunders:
-
The Plain Label Subhead: In case it bears repeating, never bore your readers. Labels are boring. Treat your subheads like mini-headlines and make sure they invoke curiosity.
-
The Spoiler Subhead: Don’t give away too much in your subhead. If you do, readers will feel no compulsion to read the rest of your text.
-
The Cryptic Subhead: Don’t try to be too clever. Readers don’t like to play guessing games. Adding curiosity should never come at the expense of clarity.
Example:
Let’s say you’re writing a post about the impact sleep has on anxiety levels and you include the following subheads:
See how the first subhead is way too plain, the second gives too much away, and the third, well, it probably made no sense to you, right?
The subheads below would do a better job at grabbing readers:
-
The Easiest Way to Reduce Daily Anxiety
-
How to Beat Anxiety Without Resorting to Medication
-
The One Thing You Must Avoid to Sleep Better
#3. Compare Each Subhead to Your Main Headline
Each subhead should clearly deliver on the overall headline of your post.
Again, if you’re viewing subheads as pit stops, they must all lead to the ultimate destination — what was promised by your headline.
If the subheads get off track and move away from that destination, readers are left feeling lost and confused.
In that case, either the subheads need to change or the headline needs rethinking.
Example:
Say you’re writing a post called “How to Silence Your Nagging Inner Critic” and you include the following subheads:
The fourth subhead’s sudden twist in topic is jarring. It does not deliver on the overall headline, which had nothing to do with your day job.
Perhaps you intended all along for the post to be about not letting doubts stop you from following your dreams and quitting your day job, but readers scanning subheads will not understand that.
They will simply feel confused.
#4. Follow a Format
If you are listing various “ways,” “steps,” “methods,” “signs,” etc., to achieve what the headline of the post promises, keep the format consistent.
If you don’t, the post comes across as unpolished. Bloggers overlook this all the time, but it’s easy to fix once you’re aware of it.
If you separate your subheads from the post and list them back to back, you can see if any stray from the course.
Example:
Say your post is called “12 Ways to Cure Insomnia” and you have a subhead for each of the 12 ways. You’ll want those subheads to follow a consistent format.
Let’s say your first few subheads read as follows:
-
Exercise Every Morning
-
Avoid Caffeine Like the Plague
-
Wake Up at the Same Time Everyday
-
There is Nothing More Sleep-Inducing Than Nighttime Meditation
Something there feel a little off?
The first three subheads start with an action verb instructing readers what to do. They are also fairly consistent in length.
But then the fourth subhead suddenly changes the format and breaks the flow. It doesn’t start with a verb and it’s much longer than the others.
This inconsistency may seem fairly innocent, but it’s distracting to readers.
Content Rule #2. Unleash the Unexpected
Let’s face it, readers today are info-holics. We all are.
So tired old advice isn’t going to cut it. Your post must be unique, bold, and eye-opening.
My advice? List your main points and see if you can add a unique perspective, experience, or twist to them. Something readers aren’t expecting.
What belief systems have you learned to challenge? What do you know that most people don’t? How can you shed new light on an old problem? What methods do you use that others won’t know about?
You don’t want to go overboard just for the sake of adding shock value. Your advice must be authentic and truly helpful. But regurgitating old advice doesn’t challenge you as a writer, nor does it enlighten your audience.
So pour your readers a little espresso for their info-hangover by delivering the unexpected.
Example:
Countless articles have been written about blogging, but how many have called you out for being dumb or told you to replace your friends?!
Jon does just that by knocking you over the head with some hard truth bombs about what it takes to make it as a blogger.
Content Rule #3. Follow a Formula
Notice how this post follows a pretty consistent formula?
Each section is relatively similar in length. Every subhead follows a pattern. Each section ends with an example.
The more consistency you weave into your posts, the better the reader’s experience.
Let’s say you write a list post covering five steps to achieve something. If the first step is 500 words, the second and third steps are 100 words, the fourth step is 200 words and the fifth step is 400 words, it looks sloppy. As though you didn’t bother to proofread it before hitting publish.
Your readers deserve the best, and minor details like this matter as they affect the fluidity of their experience.
Want to go even more pro? Look at the beginning, middle, and end of each section you write, and create a guiding formula. Perhaps you start each section with a bold statement or personal experience. Then you flesh out your advice in the middle. And then you end each section with a one-sentence call to action.
The more formulas you add to your posts, the easier they are to write and the more they look like polished works of art.
Example:
In his post on getting traffic from Twitter, Brian Honigman uses hashtags for each subhead, each section is consistent in length, and each includes a graphic.
Readers know exactly what to expect from each section, making for a fluid reading experience.
Content Rule #4. Be Ridiculously Generous
Many bloggers worry about giving away too much in their posts. After all, they want readers to sign up for their paid coaching calls or products.
So they hold back, barely skimming the surface of their advice.
Truthfully, if you’re not generous with your readers in your posts, they won’t get a good impression of your paid products.
Don’t hold back on your readers. Fully work through the problem with them. Give them complete solutions and powerful advice. Wow them with your generosity and they will stick around as loyal readers and customers.
Example:
Want to learn everything there is to know about affiliate marketing?
Holy smokes. At 10,000 words, that insanely generous post by Leanne Regalla is basically a textbook on the subject, and reader comments praise it as such. (Let’s all bookmark this one, yes?)
A post of this magnitude is quite an undertaking, but don’t let it scare you. You can also wow your audience with your generosity and thoughtfulness in a 1,000-word post.
Content Rule #5. Start and End Strong
Just as your introduction and conclusion should grab readers, you want the main body of your post to start and end strong as well.
Of course, every section should have great content, but if you’re offering five ways to achieve something, save your absolute best tips for the first and fifth ways. The first way will grab your readers’ attention, and the fifth way will leave them feeling fully satisfied.
On the other hand, if each tip successively decreases in value, readers will feel like your post is deflating. And their excitement will deflate with it.
Let’s leave readers feeling pumped when they finish your post.
Example:
Linda Formichelli gives ten crafty ways to write 1,000 words per hour.
While all ten ways are excellent, I’d argue that the first (about writing under the pressure of a full bladder) and last (about gambling with your reputation) are the most bold and attention-grabbing (bathroom break, anyone?).
Writing a Blog Post: Bonus Tip
Before writing the main sections of your post, flesh out an outline to nail your points down.
The clearer and more simplified your outline is, the more clarity and conviction your post will have.
4. Close with a Motivational Bang

We’re almost at the finish line! It’s time to close your post with a bang.
This is where you rally behind your readers. Show them that you believe in them.
Make them believe they can achieve the goal promised by your headline (because after reading your generous advice, they certainly can).
Follow these rules when crafting your motivational conclusion:
Conclusion Rule #1. Give Your Readers a Pep Talk
Motivate your readers.
Show them how far they’ve come, what they’re capable of, and what life will look like once they’ve implemented your advice.
Give them the pep talk you longed for when you were struggling with the topic your post presents.
Empower them by raising your expectations of them. They can’t just read your post and pretend it never happened — they must take action. Immediately.
Make them see that no matter what they’ve experienced or how hard they’ve struggled, their time is now.
Example:
In this post’s conclusion, Jon uses all he’s had to overcome in life to show readers that they have no excuses: no matter hard things get, they can accomplish anything they set their minds to.
He encourages readers by letting them know that he believes in them and then he raises his expectations of them by telling them they need to get started … “right freaking now.”
By the time you’re done reading the conclusion, you feel like you can conquer just about anything!
Conclusion Rule #2. Avoid New Information
A common mistake many bloggers make?
Suddenly inserting new information or tips in their conclusions.
It’s like reaching the last ten minutes of a spellbinding movie. You’re on pins and needles waiting to see how it ends, and suddenly a new character is introduced. What the … ?!
It’s jarring. Don’t do that to your readers.
Example:
In his conclusion, Robert van Tongeren motivates you to repurpose old blog posts by comparing them to epic musical classics; if they disappeared into obscurity simply because they’re old, we’d all be at a great loss.
Imagine if in the midst of such a conclusion, Robert quickly threw in one more way to repurpose content, or one small caveat to his post’s advice, or one more general tip to keep in mind?
It would throw the whole closing off and leave readers feeling ruffled instead of jamming to Bohemian Rhapsody.
How to Write a Conclusion: Bonus Tip
When writing your conclusion, put yourself back in the shoes of your readers.
What will their lives be like if they accomplish the advice in your post? How will they feel?
The more you can hone in on your readers’ point of view, the more you can motivate them to take action.
Editor’s Note:
Too many bloggers put too little thought into their closings.
That’s a shame.
Let’s face it…
Most people don’t read 100% of our posts. Heck, most people don’t even read half.
So how do we reward the precious few who read and absorbed the words we poured our heart and soul into?
With a closing we whipped together in 20 seconds.
Someone who makes it to the end of your post is primed.
They trust you. They like you. They want you to tell them what to do next.
So tell them.
Don’t waste this opportunity.
5. Polish Your Post So It’s Smoother Than a Slip ‘n Slide

Phew! You’ve written your post. Next up?
Take a well-deserved break. Step away for a day or more so you can come back to it with fresh eyes.
Once you’re ready, it’s time to do some editing. I know, the mind reels that there’s more work to do!
But editing your post is essential. If your post doesn’t provide a smooth reading experience, your reader will lose attention and bail.
Use this checklist when you’re ready to edit your post:
-
Take a Knife to It. Slash all unnecessary words, sentences, paragraphs, stories, etc. Include only what is absolutely essential to convey your message. Nothing more.
-
Motivate, Don’t Lecture. Tweak any statements that hint of being the condescending professor. Make readers feel like you’re on their side and dedicated to their success (because you are).
-
Add Emotion. Infuse your writing with passion, energy, and enthusiasm. If you’re bored by your blog topic, readers will be too.
-
Make it Easy on the Eye. Break up any large paragraphs (2–5 sentences maximum is your goal) and run-on sentences.
-
Break it Down. Clarify overly complicated wording. If you can’t say it simply, don’t write it. You don’t want to confuse your readers.
-
Speak Their Language. Add examples or metaphors to make complex ideas feel more tangible and easier to digest.
-
Check Yourself. Remove any contradictory statements or repetitive ideas (trust me, they’re there).
-
Don’t Yo-Yo. Ensure each sentence, paragraph and section drives the post forward toward the destination promised by the headline (no side routes or backtracking).
-
Be Smooth. Make each sentence and paragraph flow seamlessly into the next. Each sentence should be completely dependent on the ones before and after it or the transitions will feel choppy.
-
Avoid Sharp Turns. Adjust any abrupt changes in topic. They’re jarring to readers.
-
Keep It Real. Don’t mimic styles that don’t come naturally to you. The more you write, the more you’ll find your authentic writing voice.
-
Add Highlights. Use bold and italics to add stress where appropriate (but do so sparingly).
-
Shoot Bullets. Use bullet points to group related topic ideas and make them more digestible.
-
Spark the Senses. Be specific and concrete (describe things readers can see, feel, hear, smell or taste). Avoid abstract statements.
-
Be Firm. Avoid words like “might,” “may,” “possibly” and “perhaps” when delivering your advice.
-
Give Some Eye Candy. They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Add relevant images, screenshots, and infographics to your blog content.
-
Respect Nature. Put things in their natural order (e.g., past to present, young to old, small to large, breakfast to dinner, etc.).
-
Be Consistent. Make sure all points in a list belong to the same category; a list of steps should only list steps, a list of things should only list things, etc. This might sound like common sense, but this rule gets broken often.
-
Don’t Be Lazy. Ensure all the necessary information is contained within the post itself. (External links should only provide supplemental information. A reader shouldn’t have to click a link to comprehend your post.)
-
Kill the Weak. Eliminate weak and flabby words. Replace weak verbs (e.g., “she went”) with more concrete, visceral verbs (“she walked”), replace passive voice (e.g., “he was pushing”) with active voice (e.g., “he pushed”) and replace weak adjectives (e.g., “good”) with strong adjectives (e.g., “wonderful”).
-
Feel the Beat. Be mindful of the pace and rhythm of each section. Speed things up or add some punch with crisp, short sentences. Slow things down with longer explanations. Good writing uses both.
-
Do the Obvious. Fix any typos, spelling mistakes, or grammar mistakes (you can use grammar checkers like Grammarly and Hemingway App).
-
Be Honest. Give credit where due.
How to Edit a Blog Post: Bonus Tip
A great way to self-edit your posts is to read them out loud.
Doing so will help you catch many of the issues listed above, particularly things like overly complicated wording, run-on sentences and choppy rhythm.
Win the Battle for Your Reader’s Attention
Blogging is a battle.
A war to get your ideas the attention they deserve.
Your enemy? The dizzying array of online distractions that devour your readers.
This battle is not for the faint of heart.
There are so many learning curves. Blogging platforms and plugins you’ll need to install. Social networks you’ll need to employ. Content marketing techniques you’ll need to try.
But none of that stuff matters if you’re drowning your ideas in amateur writing. You might as well lay your sword down in defeat. Readers don’t have time for amateurs.
So before you venture any further down the blogging rabbit hole, you better make sure you know how to write a blog post like a pro.
Skip that step, and nothing can save you. Your battle is lost.
The good news is, writing good blog posts is a skill you can learn. And it’s one you must learn.
You have powerful words and ideas that can transform readers’ lives. Those ideas are worth fighting for.
So when you’re ready to enter the arena, arm yourself with this ultimate guide and fight the good fight.
Your readers are counting on you.





































