
Some of the features in the below will be introduced in the upcoming upgrades.
For over 8 years, LSIGraph has helped hundreds of thousands of users to rank on Google with LSI keywords. Whenever there were changes in Google’s algorithms, LSIGraph has always proactively adapted since day one.
LSIGraph has implemented changes that are always in line with Google’s algorithms. If you’re curious about the changes that have taken place within LSIGraph, keep reading this article!
How LSIGraph Started
Here’s a story...
Many years ago, Steve had problems with ranking on Google’s search results. He wanted to rank for his newly-created online business and hopefully get potential visitors and convert them to customers.
He didn’t do much, except add the keywords that are relevant to his products. He was also unfamiliar with all the different factors that affect rankings on Google, or SEO as a whole.
Steve reached out to Andy, who would eventually become one of LSIGraph’s most significant team members. Steve knew Andy was super into SEO, diligently learning about the different Google algorithms and how each impacted search results. Andy promised to help Steve out.
Meanwhile, Andy had his own website that was not bringing any traffic or sales. Even though he had awesome products and created great content using a content creation app, he was unable to gain enough quality visitors to turn them into leads. Apart from that, Andy also wanted to rank in the top 3 spots of SERP.
After a while, Andy uncovered the secret behind two of Google’s most prominent algorithms, Hummingbird and RankBrain. He started using Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI). This secret would, eventually, prove to be effective in helping thousands of users to rank well on Google search results.
Latent semantic indexing was originally conceived as a mathematical method in the late 1980s. The intention was to obtain accurate information retrievals. Since then, LSI has been widely implemented in uncovering the text’s meaning in response to users’ queries.
LSI keywords are keywords that are related semantically to a targeted keyword. These keywords amplified the targeted keywords and provide more contextual information to search engines and users.
With this newfound information, Andy helped Steve to pinpoint the LSI keywords to include on his website. The addition of LSI keywords in the content made the writing seem natural instead of forced.
Google’s search algorithms could also better understand the context of the pages. Steve’s website began to rank on the first page of search results. He also noticed a significant increase in his web traffic unlike any he had ever seen before:
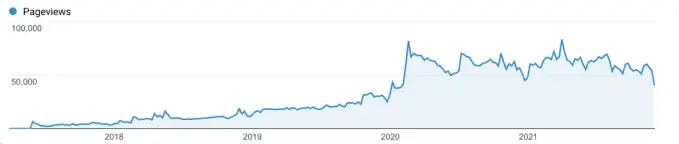
Andy also managed to turn his website around. He nabbed the 3rd spot of the SERP, eventually climbing to first place over the next few weeks. Andy’s newfound ranking also brought quality visitors to his website which in turn, translated to leads.
However, most keyword research tools did not place much emphasis on LSI keywords. Nor were the tools affordable. Realizing this gap opportunity, Andy gathered a small group of people who shared the belief that LSI keywords would be a crucial factor.
This small group of like-minded individuals would develop the first LSI keyword research tool. And that tool is what you recognize as LSIGraph.
LSIGraph is a keyword research tool with its very own developed semantic analysis. This analysis seeks to understand the meaning behind each search query, and will suggest users with the best LSI keywords that match those search queries.
Over the years, LSIGraph has consistently improved its algorithm so it was able to grasp the meaning behind search queries and offer keywords, even if they are not exact matches. These keywords may be synonyms, co-occurring terms, or implied words. They are all easily retrievable from the algorithm.
From the first day till now, LSIGraph has been proactively adapting to the changes in the core Google search algorithms. To get an idea of the changes LSIGraph has adapted to, let’s first look at the past Google algorithms that have been majorly impacted search.
Advancements in Google search algorithm
Every day, 15% of search queries have never been seen by Google.
For queries that are longer, conversational in nature, or contain prepositions that affect the queries’ meaning, it may be harder to interpret their meaning or intent. If Google were to rely solely on understanding the meaning of the keywords within the query, it’s possible that they may not provide search results that are relevant.
Google has introduced several algorithms. From Hummingbird to RankBrain, each algorithm has always placed great emphasis on understanding search queries. With the release of BERT, Google AI can now consider the full context of words in searches by looking at the words that come before and after them.
All of these algorithms have one sole intention. That is to provide the most relevant results to users based on their queries.
Let’s take a brief look at some of these algorithms, and how LSIGraph has adjusted to the changes.
-
Hummingbird
The release of Google Hummingbird in 2013 signified Google’s commitment to learning the intent of search users’ queries to match their search queries to more relevant results. The algorithm also looked deeper at the content of individual pages of a website so lead users directly to the most relevant page.
Before the Hummingbird update, Google looks at search queries too literally. For example, if a person was to search for “nba score”, Google would display search results that contain the keyword.
Now, the Hummingbird update has allowed Google to understand the underlying intent behind the query. If the same person was to look up “nba score”, here’s what would be displayed on search results:
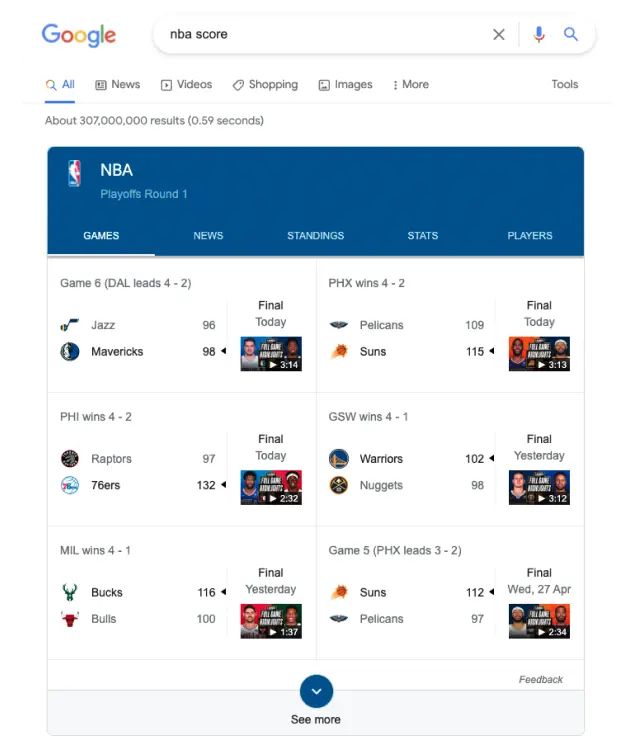
Here’s what you’ll see when you search for “nba score” on Google! Google Hummingbird also positively affects long-tail keywords. This is because Hummingbird also considers the context and meaning of the whole query over individual words. Thus, writers and webmasters were encouraged to optimize their site and content with natural language instead of attempting to force keywords in.
How LSIGraph Adapted
To assimilate into this, LSIGraph has developed a new AI model. This machine learning model is able to understand the context of search queries and their underlying intent. With this AI model, you will not only get accurately relevant keyword data. You will also get related keywords that are similar to Google’s SERP.
This AI model has also been trained with natural language processing (NLP). With this training, LSIGraph is able to understand search queries naturally. LSIGraph will also be able to provide users with keywords that would answer these search queries.
LSIGraph has also improved on its Latent Semantic Value (LSV), which was developed early on from the beginning of the tool. LSV helps you choose the best keywords you should include when optimizing your content. You will have an estimate of a keyword’s true value.
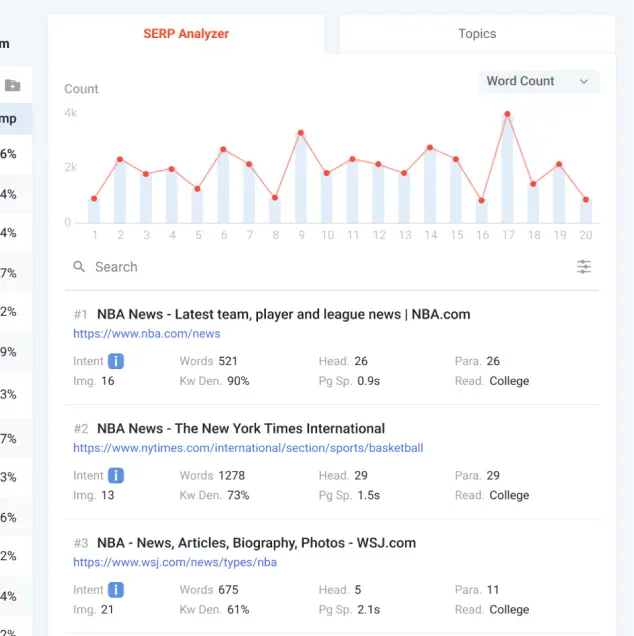
LSIGraph’s SERP Analyzer LSIGraph’s SERP Analyzer will display the top 10 articles on the search results. You can identify the intent of those content, as well as the overall content brief. With this feature, you can understand how Google looked at the underlying intent behind the keywords.
-
RankBrain
In 2015, Google released another algorithm. It is an AI that helps Google process and understands search queries. Queries are passed through an interpretation model to identify the true search intent.
Factors like the searcher’s location, personalization, and the words used in the query are considered when determining the searcher’s true intent. Using this information, Google can deliver more relevant results.
RankBrain is considered the third most important ranking factor in Google’s ranking algorithm, behind content and links. RankBrain will be given a bundle of previous searches to learn by matching search results.
Google RankBrain understands the relationships between words excellently. Words like “the”, “and”, “without” may provide a different meaning or intent behind a user’s search query. And RankBrain is able to understand these meanings.
RankBrain’s ability to analyze patterns between searches, even if they may seem unrelated, is unparalleled. This makes it highly effective at handling search queries or keywords that have never been seen by the search engine.
If the search query is new or unfamiliar, RankBrain will display a group of search results that would be most relevant. How users interact with the results determines the ranking of those pages for that particular search query.
RankBrain has helped the Hummingbird algorithm to provide more accurate results. This is because RankBrain can learn words and phrases that Hummingbird may not know. RankBrain can also learn words and phrases that are specifically used in a country or a language.
How LSIGraph Has Adapted
In LSIGraph, a new classification model is developed to better identify the user intent of keywords and the SERP. With this model, you can now discover the semantic classifications and search intent of the keywords in LSIGraph.
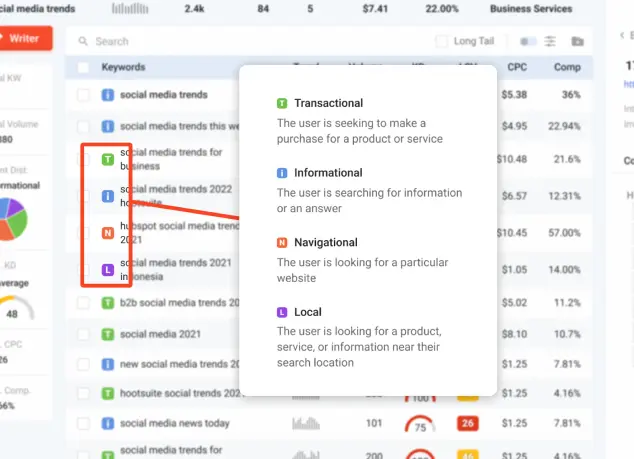
Categorizations of user intents in LSIGraph LSIGraph also allows users to set the location and language of where they intend to research their keywords. Location of search and intent are factored in when providing data that are accurate and relevant.
For keywords that may be new or unfamiliar, LSIGraph will also display keyword data that will be most relevant and related. These include results shown under SERP Analyzer and Topics.
-
BERT
In October 2019, Google announced and rolled out a new algorithm: Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, or BERT. It is a neural network-based technique for natural language processing (NLP) pre-training that is open-sourced.
BERT is built upon previous work in pre-training contextual representations. But, most language models could only read text input either from left-to-right or vice versa. They could never read in both directions at the same time. BERT is designed to read in both directions simultaneously.
BERT is pre-trained on two strategies: Masked LM (MLM) and Next Sentence Prediction (NSP).
In Masked LM, 15% of the words in each sequence are replaced with a [MASK] token. BERT then tries to predict the value of the words based on the context provided by other words in the sequence.
In Next Sentence Prediction, the BERT model is given pairs of sentences. In the training, BERT learns to predict if the following sentence is connected to the first sentence. MLM and NSP are trained together to minimize the combined loss function of the two strategies.
BERT considers the full context of a word by looking at other words that are before or after it. This is incredibly useful to understand the intent behind those search queries. A deeper understanding of the context of the search query will allow Google to provide highly relevant results.
A powerful trait of BERT model is it can learn from one language and apply the knowledge to other languages. This helps Google to return even more relevant and accurate results in various languages.
BERT model is also used to improve featured snippets results. Huge improvements have also been seen for featured snippets in other languages like Korean, Hindi, and Portugese.
These three algorithms share one common goal: to understand the intent of a search query and provide results that are relevant to users.
Hence, Google’s ranking algorithms have slowly moved beyond looking at keywords and their semantics. They seemed to have shifted their focus towards understanding the overall contextual query - mainly due to BERT.
To understand these contextual queries, Google looks at the entities in search queries. Entities, as defined by Google, are “a thing or concept that is singular, unique, well-defined, and distinguishable.”
Entities can be both nouns or abstract concepts. They are often defined and are independent of other entities or keywords. Google will graph and store the meanings and knowledge of these entities in a database known as Knowledge Graph. The Knowledge Graph allows Google to answer factual questions posed by search users.
Google’s increasing emphasis on entities over keywords has allowed them to provide more accurate results. Keywords containing context will help define your entities. And when you add context to your content, you build a relationship between the entities in your content.
The relationship between entities in your content is highly significant in informing Google that your content answers the intent of a user’s search query. The better Google can understand your content, the higher your chances are to rank high.
In order to highlight these relationships, you must write the content splendidly. It does not only need to be great in delivering the necessary information, but it should also sound natural. If you manage to fire on both cylinders, then you’ve truly got great content at hand.
How LSIGraph Has Adapted
As Google’s focus has tremendously changed for search results, LSIGraph has also adapted and made massive improvements and adjustments.
The LSIGraph team has created a new algorithm and a machine learning model that’s integrated with BERT. This AI model is able to identify the full context of an entity as well as the relationship between entities.
The classification model that was previously developed to identify users’ intent has also been integrated with BERT. Whatever the user intent is (informational, transactional, etc.), LSIGraph will now display the list of keywords along with their right intent.
LSIGraph has also developed another new algorithm. This algorithm functions to pinpoint the entities that are within keywords. LSIGraph will then create clusters of relevant entities based on the identified entity, forming topical clusters.
These topical clusters will cover an extensive range of topics that you can include in your content. You no longer need to scratch your head wondering what topics you should add or if they are related to the content.
These topical clusters are a new feature that has been added in LSIGraph. The clusters are shown as you continue with your keyword research.
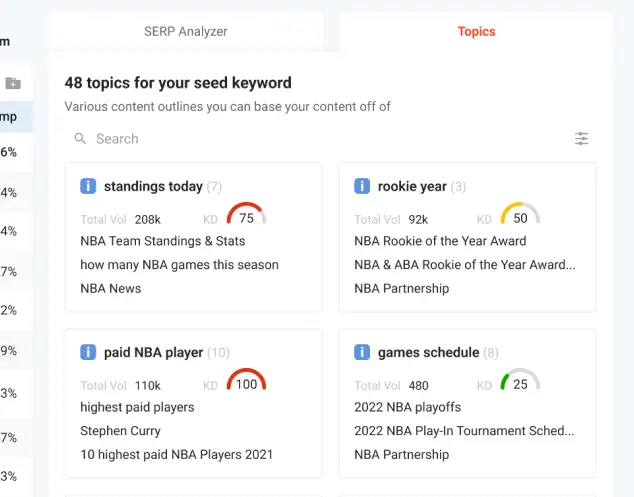
Keyword clusters that are based on the seed keyword “nba score” Content Writer has also been significantly improved. Multiple features have been added inside to assist as you write your content. These features include SERP Analyzer, Topics, and Popular Questions.
The team has also added a new writing score mechanism for LSIGraph’s content writing module. The mechanism accounts for the total usage of the contextual keywords you added to your content.
The scoring mechanics will analyze the draft content and assess how optimized it is for on-page SEO. Therefore, it will notify you if you have included too many contextual keywords in the content (aka keyword stuffing).
Creating Great Content That Ranks
Everyone wants great content that ranks at the top of the SERP. It’s where one generates traffic and leads, and converts them into sales or revenue. But with the release of RankBrain and BERT, writers have to be wary of the way they write and ensure that it often sounds natural.
Thus, what are the right and simple ways to have content that ranks easily?
You will first need to understand what is the user intent behind the targeted search query. For instance, if they are looking for information on a query, your content should provide the information and facts users are looking for.
When you include topics that have different intents, it creates a bit of confusion. Google will not understand the intention of your content. As a result, your content may not rank as high on Google SERP.
Let’s look at a quick example. A search user intends to look for information on used cars. They found a webpage on the first page of search results that seems relevant and clicked on it. But instead of getting information about used cars, the page talks more about where they can purchase highly affordable secondhand cars.
As the webpage did not provide the relevant information, the user will immediately go back to search results. That gives Google an indication that the webpage does not answer the intent of the search query.
To eliminate the assumptions and guesswork in identifying the search intent of each result in the SERP, you can use LSIGraph’s keyword research tool. Look up the keywords you would like to target and identify their search intent.
For instance, when you look up the keyword “social media trends”, it will show you the classified user intent beside the keyword. If you’re curious about the intent of other top-performing results, you can look at the SERP Analyzer to look at the top 10 results and what their user intent is.
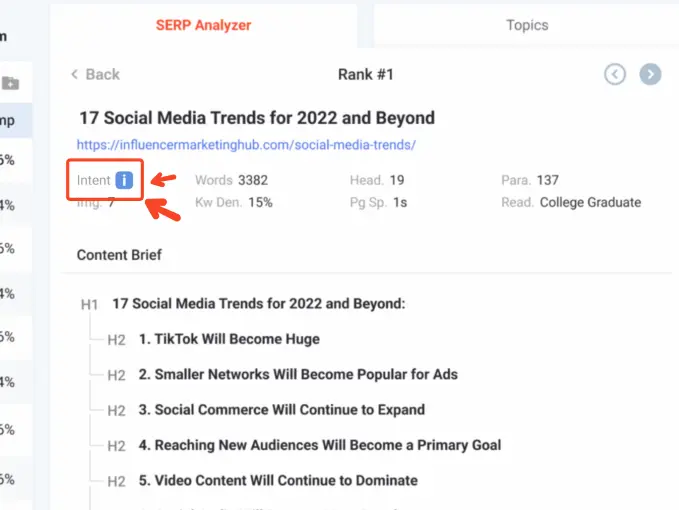
Hover over to the “Topics” tab to see the possible keyword clusters that you should include in your content. These clusters would provide more context on the topic you’re writing about as a whole.
Select the keywords that are aligned with your targeted keyword’s intent. This way, you’ll have a strong topic with keywords that are both relevant and provide a clear context to both your audience and Google.
Once you’ve performed your keyword research and prepared your content outline, you can start writing your content. You can also use LSIGraph’s Content Writer, another built-in module that pairs seamlessly with the keyword research tool.
Write your content based on the topic outline and keywords that you have researched. If you’re unsure of what to write, Content Writer offers you an extensive list of information and references that top-performing results have been using to their success.
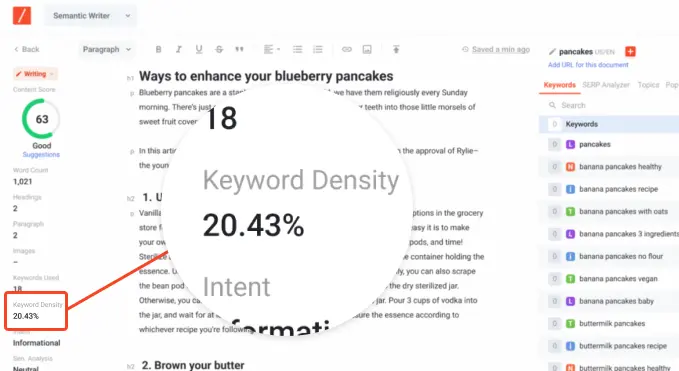
As you curate your content in Content Writer, be sure to include your target keyword and other contextual keywords in the content. But don’t overdo it! Remember that Google is looking at content that’s written naturally instead of being forced.
Maintaining a low keyword density will also push your on-page SEO to be better, which is good for your SEO overall (A good keyword density is between 2 to 5%). You can view your keyword density score as a measure of whether you are stuffing your keywords into your content or not.
Once you’ve written your content, it’s time to publish it on your website! And there you have it, that’s how you can produce a great content that will rank well on Google’s results.
Measuring Great Content That Ranks
How do you know if your content is good enough to get ranked? Truthfully, that’s a hard question to answer. It can take days, even weeks, before you can evaluate the performance of your content.
But if you have used a content writing tool (like LSIGraph’s Semantic Writer), you will know whether your content is ready to fight with your competitors for the same keywords.
In Content Writer, you will view the content scoring of your draft as you write. The content score is an indicator of how relevant your content is to the keyword that you’ve targeted.
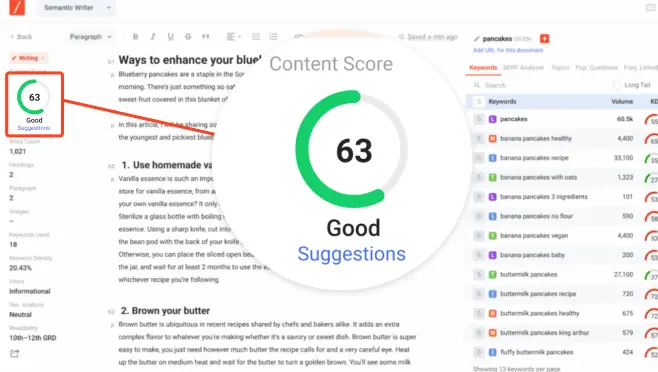
This content scoring will update you as you write. If your content is going off-course contextually, you will immediately know and make adjustments to your content. When you have a great score, you will then know that you have your content ready to fight amongst the best for the top rankings.
Besides having a scoring mechanism solely for looking at the context of your content, you should also ensure that it’s optimized for on-page SEO. In simpler terms, on-page SEO is optimizing the webpage content for search engines and its users.
To ensure that your on-page SEO is in tiptop shape, ensure your targeted keyword is used in...
- Title
- Meta description
- Headings
- Paragraphs
- Alt text in the images
- Link anchor text
- URL of your webpage
On-page SEO score also considers the user experiences of your readers as they stumble upon your content. Ensure your page loads fast, content-to-query relevancy (remember keyword stuffing?), the content is easily readable, and has a clean layout that does not distract users from your content.
If users dwell long on your content, it tells Google that search users are finding your content valuable and informative enough as it answers the query they are searching.
When you’ve nailed all of these points, you do not need to be as worried as you have gotten the fundamentals down. So sit back, have a glass of wine, and make a toast as your content starts climbing up the SERP.
Conclusion
Google updates and algorithms have always served as an indication and direction on where SEO is headed. Neglecting or not taking any action to the changes will only harm your existing and new content.
In the past, Google algorithms have focused on the importance of LSI. LSIGraph has been fortunate enough to be the first and top tool to provide LSI keywords that are proven effective for Google’s results.
Even as Google rolled out significant algorithms and updates that affect search, LSIGraph has also consistently and proactively reacted to the changes in order to serve you better with keywords that bolster your rankings.
Now, as Google fully shifts its focus towards understanding the context of the queries, LSIGraph will also be pivoting towards contextual keywords. With new algorithms and AI models to better understand the relevance of contextual keywords, LSIGraph is primed to provide you with the keyword data and writing assistance you need to get your content at the top of the SERP.
One thing’s for certain:
LSIGraph’s mission has never changed in the last 8 years. And that is to empower your content with keywords that help you rank on search engines.
See you inside.



